Card payments are temporarily suspended for technical reasons! Please consider paying with cryptocurrencies with 15% off.
Card payments are temporarily suspended for technical reasons! Please consider paying with cryptocurrencies with 15% off.
days left

AUTHENTIC PRODUCTS
Only original pharmaceutical products that passed 3 stages of clinical trials.

GMP QUALITY
Our products are produced on GMP or state licensed factories.

10% CRYPTO DISCOUNT
10% discount for paying in BTC or other cryptocurrency.

PAYMENT BY CARD
Convenient Payment by Visa or MasterCard.

GUARANTEED DELIVERY
Guaranteed delivery times and clear Reshipment & Refund Rules.

PROMPT SHIPPING
Different shipping methods and same or next day shipping.
CAFFEIN-ACTIV ® (Caffeine + B12)
0 Reviews
Caffeine is a substance that in its natural form is produced in the leaves and seeds of many plants. In addition, it is often found in worldwide popular drinks – coffee, tea, many soft drinks, as well as most energy drinks.
Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, increases mental and physical performance, and physical activity, shortens the reaction time, temporarily reduces fatigue and drowsiness, facilitates perception, increases heat production and urination, and increases gastric secretion. It may be used as an extra energy source in the morning, as well as to stay productive during the day.
Caffeine has medicinal properties and is used as a stimulant of the central nervous system, causing increased activity. Most people react to caffeine with increased energy and improved mood.
Blood pressure changes under the action of vascular and cardiac mechanisms of caffeine: at normal arterial pressure, caffeine slightly increases or does not change it, and at arterial hypotension, it normalizes it.
Sensitivity to caffeine is different for everyone and often depends on age. The younger a person is, the less substance is needed to feel the effect. Our body quickly absorbs caffeine and quickly gets rid of it. Caffeine can enter the body through the mucous membranes of the cheeks. For this reason, chewable tablets containing it begin to work much faster than coffee, for example. In the form of a drink, caffeine must first pass through the stomach and intestines, and only after that enter the blood.
The tablets also contain Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin). Its main function is the normalization of blood formation processes and participation in the formation of red blood cells. B12 also has a beneficial effect on fat metabolism in liver tissues, reduces cholesterol in the blood, normalizes the state of the nervous system, and metabolic processes in the body, protects nerve cells
Intended effects:
- Energizing;
- Improves mood;
- Normalizes hypertension;
- Improves perception and memorization;
- Temporarily reduces fatigue and drowsiness.
Produced by Kvadrat C / Vitamir, Russia.
To be used as a dietary supplement. It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Legal Disclaimer
This product has not been approved by the US FDA. All statements on this page are for informational purposes only and have not been evaluated by the US FDA.
This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. See more
Contents
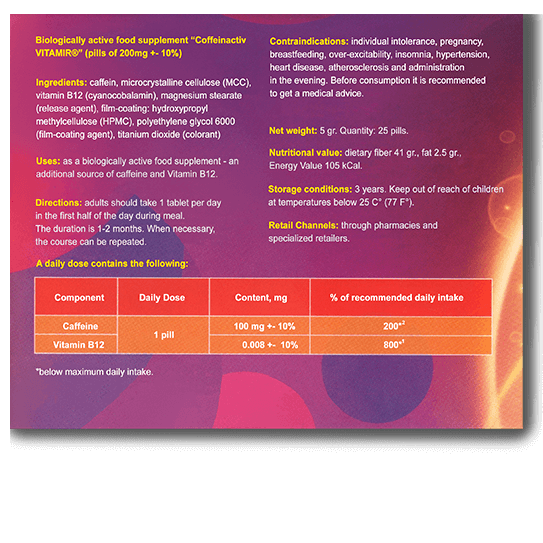
Ingredients: caffeine, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) (carrier), vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), magnesium stearate (anti-caking agent).
Dosage and administration
Adults 1 tablet in the morning, with meals. The duration of treatment is 1-2 months. If necessary, the course can be repeated.
Indications
Recommended as an additional source of caffeine, vitamin B12.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to the components of dietary supplement, pregnancy, breastfeeding, increased nervous irritability, insomnia, hypertension, impaired cardiac activity, marked atherosclerosis, taking in the evening.
Manufacturer
To be used as a dietary supplement. It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
- C Ashton et al (1987) Caffeine and health https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1248372/
- T Chou (1992) Wake up and smell the coffee. Caffeine, coffee, and the medical consequences https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1022034/
- Ohnaka et al (2012) Effects of 16-Week Consumption of Caffeinated and Decaffeinated Instant Coffee on Glucose Metabolism in a Randomized Controlled Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3502017/ - Bae et al (2014) Coffee and health https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5481750/
- Cappelletti et al (2015) Caffeine: Cognitive and Physical Performance Enhancer or Psychoactive Drug? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462044/
- Schliep et al (2016) Serum caffeine and paraxanthine concentrations and menstrual cycle function: correlations with beverage intakes and associations with race, reproductive hormones, and anovulation in the BioCycle Study https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4919523/
- Poole et al (2017) Coffee consumption and health: umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomes https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5696634/
- Weseelink et al (2017) Caffeine and caffeinated beverage consumption and fecundability in a preconception cohort https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4907331/
- Temple et al (2017) The Safety of Ingested Caffeine: A Comprehensive Review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5445139/
- Chang et al (2018) Caffeine Caused a Widespread Increase of Resting Brain Entropy https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209050/
- Evans et al (2019) Caffeine https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519490/
- Collado-Mateo et al (2020) Effect of Acute Caffeine Intake on the Fat Oxidation Rate during Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33255240/
- Ősz et al (2022) Caffeine and Its Antioxidant Properties-It Is All about Dose and Source https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36361861/
- Ruggiero et al (2022) Neurodegenerative Diseases: Can Caffeine Be a Powerful Ally to Weaken Neuroinflammation? https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36361750/
- Wang et al (2022) Effects of Caffeine Intake on Endurance Running Performance and Time to Exhaustion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36615805/
- Ferreira et al (2022) High Doses of Caffeine Increase Muscle Strength and Calcium Release in the Plasma of Recreationally Trained Men https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36432607/
0
Based on 0 Reviews
(0)
(0)
(0)
(0)
(0)
Thank you!
You will now receive regular updates from us!
Your coupon