Comprehensive Cortexin Review 2022: Research, Mechanism of Action, Intended Uses, Alternatives, FAQs
May 17, 2022
In this article, we once again turn to the Russian literature on nootropic drugs. This time we want to make Cortexin review and talk about the book dedicated to Cortexin. But before that let us start with answering the question: What is Cortexin? ⬇️
CORTEXIN REVIEW: LIST OF CONTENTS
- What is Cortexin?
- Cortexin Composition
- What are Cortexin Benefits?
- Cortexin Indications for Use
- Cortexin Research
- Cortexin Dosage
- How to Prepare Cortexin Solution?
- How to Inject Cortexin?
- When Will I Feel The Effects of Cortexin?
- What are Cortexin Side Effects?
- Can I Be Allergic to Cortexin?
- Cortexin and Alcohol
- Cortexin Drug Interactions
- Cortexin or Cerebrolysin?
- Facts about Cortexin Producer
- Anecdotal Cortexin Reviews
- Official Drug Sheet of Cortexin
- Bibliography
WHAT IS CORTEXIN?
This is a drug from the group of nootropics, a mixture of neuropeptide fractions, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, obtained from the cerebral cortex of cattle. It has a pronounced but subtle positive effect on the brain.
It is interesting to note that initially Cortexin was aimed at treating defense officials. It was developed in the Military Medical Academy in Saint Petersburg, in Russia, specifically for these purposes. But since 1999, Cortexin has been produced industrially through the patented technology.
Now it is a popular peptide nootropic used to treat the brain.
WHAT IS CORTEXIN COMPOSITION?
Cortexin is a bovine brain lyophilisate. It means that it is produced from the cerebral cortex. And the cerebral cortex is a highly saturated “collection” of various chemical structures.
Studies single out a wide variety of proteins in membrane fragments and intracellular structures, including such functionally important ones as calmodulin-adenylate cyclase, neurotransmitter enzymes, proteins of receptors and various kinases, etc., as well as vitamins, gangliosides, phospholipids, sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium ions, and other elements.
Although the analysis of the pharmacokinetics of the whole range of substances that make up Cortexin is not possible, in general there are low molecular weight polypeptide fractions, amino acids, vitamins, and trace elements in its chemical structure. [17]
POLYPEPTIDES IN CORTEXIN COMPOSITION [16]
Polypeptides are compounds of 10-20 amino acids. They are small in size and weight (up to 10kDa).
Lyophilization is used to obtain such a mixture. This is a special patented method in which the biological properties of substances are better preserved. Allergic reactions are said to be less likely with this method in comparison to conventional preparation of medicines.
Lyophilisate is obtained from the original substrates by a special “soft drying” of the substance. It is first frozen and then placed in a vacuum chamber, where the drug transitions from a solid state to a gas, bypassing the liquid state.
Due to this, proteins and amino acids necessary for the manufacture of the medicine are not destroyed. This is important since the function of the resulting neuropeptides depends on the integrity of their structure.
Due to the small size of the polypeptides in Cortexin, the drug easily penetrates the barrier between blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a fluid that circulates around the brain. Thus, the drug reaches the nerve cells – neurons. Neurons in turn communicate with each other using special substances called mediators.
Mediators are peptides that stimulate or inhibit neighboring cells. Due to the fact that Cortexin has a similar structure, it triggers the release of the body’s own peptides. As a result, the balance between different fractions of mediators is optimized.
In addition to polypeptides, the drug contains an auxiliary substance – glycine, which acts as a stabilizer.
L-AMINOACIDS IN CORTEXIN COMPOSITION [2]
In particular, Cortexin peptides contain at least two stimulating amino acids – aspartic acid (446 nmol/mg) and glycine (298 nmol/mg). In addition to the mentioned above, the following amino acids are presented in Cortexin:
- threonine (212 nmol/mg);
- serine (268 nmol/mg);
- glutamic acid (581 nmol/mg);
- proline (187 nmol/mg);
- alanine (346 nmol/mg);
- valine (240 nmol/mg);
- isoleucine (356 nmol/mg);
- tyrosine (109 nmol/mg);
- phenylalanine (162 nmol/mg);
- histidine (116 nmol/mg);
- lysine (253 nmol/mg);
- arginine and other amino acids (202 nmol/mg).
Thus, the share of aspartic acid accounts for up to 12%, and glutamic acid – about 15% of the total amino acid content of Cortexin. The drug does not contain methionine.
VITAMINS IN CORTEXIN COMPOSITION [2]
Cortexin contains a number of vitamins, in particular:
Water-soluble:
- thiamine (vitamin B1) – 0.08 μg / 10 mg,
- riboflavin (vitamin B2) – 0.03 μg / 10 mg,
- niacin (vitamin B3, vitamin PP, niacin) – 0.05 μg / 10 mg;
Fat-soluble:
- retinol (vitamin A) – 0.011 μg / 10 mg,
- alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) – 0.007 mcg / 10 mg.
MICROELEMENTS IN CORTEXIN COMPOSITION [2]
In addition to five essential vitamins, Cortexin contains many minerals (macro- and microelements):
- copper (Cu): 0.2129 μg / 10 mg;
- iron (Fe): 2.26 μg / 10 mg;
- calcium (Ca): 22.93 μg / 10 mg;
- magnesium (Mg): 8.5 μg / 10 mg;
- potassium (K): 19.83 μg / 10 mg;
- sodium (Na): 643.2 μg / 10 mg;
- sulfur (S): 152.65 μg / 10 mg;
- phosphorus (P): 91.95 μg / 10 mg;
- zinc (Zn): 4.73 μg / 10 mg;
- molybdenum (Mb): 0.0203 μg / 10 mg;
- cobalt (Co): 0.0044 μg / 10 mg;
- manganese (Mn): 0.0061 μg / 10 mg;
- selenium (Se): 0.0745 μg / 10 mg;
- aluminum (Al): 0.3104 μg / 10 mg;
- lithium (Li): 0.0340 μg / 10 mg.
There is reason to believe that the positive effects of the drug are explained not only by the action of the polypeptides of the indicated amino acid composition but also by the neurochemical activity of macro- and microelements contained in the drug, as well as vitamins A, E, B1, and PP.
WHAT ARE CORTEXIN BENEFITS?
Cortexin has many positive effects. Therefore it is used in the treatment of many neurological diseases. The drug will be useful both in the acute phase of the disease and in the recovery period.

According to the manufacturer, the drug has shown the following effects:
- Neuroprotective. Cortexin can protect nerve cells from aggressive influences: microbes, toxins, lack of oxygen and nutrients;
- Regenerative. It has the ability to accelerate the healing of damaged body tissues;
- Metabolic. Cortexin is known to improve oxygen supply and neuronal nutrition;
- Antioxidant. The drug can slow down the processes of fat peroxidation, during which free radicals are formed, the excess of which damages tissues. Due to this mechanism, the resistance of neurons to a lack of oxygen increases.
- Antiepileptic. It is said to reduce the likelihood of developing epileptic seizures. This is possible due to the ability of the drug to normalize the ratio between excitatory and inhibitory substances in the central nervous system. Thus, the risk of developing areas of excessive excitement, which represent the basis of epileptic seizures, can be decreased.
- Nootropic. There is a positive effect on cognitive functions: memory, attention, and concentration. These processes are based on the interaction of nerve cells with each other. Cortexin is known to accelerate this interaction.
CORTEXIN: USES INDICATIONS
Cortexin is most often used in the treatment of the following pathological conditions:
- Cerebrovascular diseases, including stroke and its consequences;
- Inflammatory brain diseases such as neuroborreliosis, encephalitis, myelitis, and encephalomyelitis;
- Epilepsy;
- Traumatic brain injury and its consequences;
- Cognitive disorders, for example dementia, delirium, mental retardation, etc.
- Pediatrics: psychomotor and speech retardation in children and reduced learning ability, as well as ADHD.
There is even evidence that Cortexin may relieve post-COVID syndrome. [19]
CORTEXIN: RESEARCH & STUDIES
In 2005 GeroPharm published a book collecting the works of 43 authors who have shared their studies on Cortexin in neurology, neurological intensive care, neurosurgery, neonatology, pediatrics, infectious diseases, psychiatry, and toxicology. Below you will find the book heading. The main pages are in Russian. But we have provided the translation of the results of several studies.
Please let us know if you want to look into any particular abstract of the book. By the way, if you are interested in scientific literature about nootropics, take a read of our post about the Book on Nootropics. It was written by Dr Arushanian a distinguished Soviet and Russian professor. And we translated it into English so that all the nootropics enthusiasts could have access to this unique information 👍🏻
CORTEXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT

Cognitive impairment is a disruption in the cognitive functioning of the central nervous system, which includes higher cerebral activity, and higher mental and cognitive functions. These are the processes in the brain with the help of which the study of the surrounding world and analysis of the incoming information takes place.
There are three degrees of severity of cognitive impairment:
1) Severe disorders of cognitive processes, leading to the inability of a person to conduct normal activities, work and control themselves. Examples of such disorders are dementia and delirium.
2) Medium disorders – significant changes in higher brain functions. Patients can serve their own basic physiological needs and do not experience problems when communicating with others. Without proper treatment, there is a high risk of worsening the condition to a severe degree.
3) Mild disorders – a slight impairment of cognitive processes, in which it is possible to carry out normal daily activities, and perform professional and household duties. Such disorders occur in many diseases and are not always caused by damage to nerve structures.
HOW TO TREAT COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT?
The treatment of all cognitive disorders is aimed at eliminating the cause of this condition, be it a stroke, a TBI, or others. Another area of therapy is the restoration of higher brain functions to the original level.
In 2012, the results of a multicenter, randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the safety and efficacy of Cortexin in the acute and early recovery period of hemispheric ischemic stroke, which is one of the common causes of cognitive complications, were published. The study included more than 270 patients and was carried out in 7 regional specialized centers for the treatment of vascular pathology.
The high efficacy and safety of repeated courses of Cortexin have been proven in comparison with a single course of treatment and with a placebo. Cortexin application in two courses 10 days each contributed to both the restoration of daily activity and more complete recovery of the patients’ cognitive functions. This study confirms the high rehabilitation potential of the drug. [5]
It is important to note that treatment of cognitive impairment shall be comprehensive. The patient needs special gymnastics, massages, and classes with therapists. The support of family and friends is of great importance for the normalization of the patient’s mental status.
The following medical methods are commonly included in the treatment:
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors;
- Reversible blockers of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors;
- Neuroleptics;
- Metabolic and vasoactive drugs;
- Nootropics.
Cortexin is a nootropic agent. It improves the interaction between neurons by normalizing the ratio between excitatory and inhibitory mediators. [2] The recommended course of administration is 10 days, 10 mg daily in the morning. For more information on how to use Cortexin and the recommended dosages, go to this section of the article.
Also please remember that cognitive impairment is not an autonomous disease. This is a symptom of other diseases. Therefore, when disorders of higher nervous functions appear, it is advised to consult a doctor as soon as possible in order to identify the cause of such changes. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the faster the treatment will begin and the more chances there are for the patient to recover.
CORTEXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ENCEPHALOPATHY
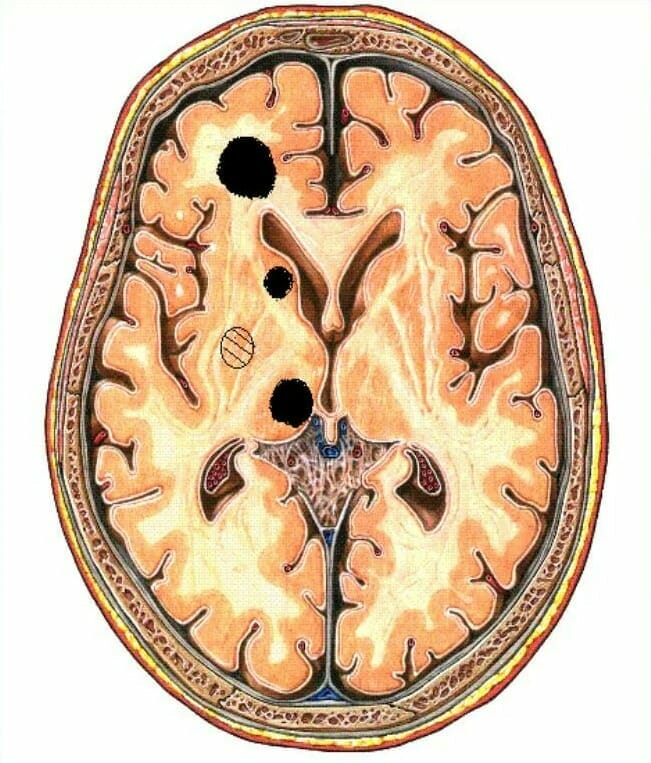
WHAT IS ENCEPHALOPATHY?
Encephalopathy is a general name for a group of different conditions in which non-inflammatory brain damage occurs. The role of the main damaging factor belongs to a metabolic disorder of nerve cells, which leads to their death. There are 2 types of encephalopathy: perinatal and acquired.
Perinatal encephalopathy is a disorder in the structure of the brain that occurs during the period from 28 weeks of intrauterine growth till the first week of life. Сlinical manifestations of this condition are noticeable from birth.
Acquired encephalopathy is more common in adults. It is usually secondary to other diseases. Risk factors for the appearance of this pathology can be:
- Infectious diseases;
- TBI;
- Exposure to endotoxins (in acute pancreatitis, hepatic and renal failure);
- High blood pressure;
- Sedentary lifestyle and bad habits;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory system;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Long-term lack of vitamins, proteins, fats or carbohydrates, etc.
The complexity of diagnosis lies in the fact that at the initial stages of the disease there are no specific symptoms by which it can be suspected. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination: laboratory analyses of biological fluids, instrumental diagnostics (MRI, echoencephalography, etc.), as well as consult with several specialists: therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist.
HOW TO TREAT ENCEPHALOPATHY?
The treatment is aimed at eliminating the disease that caused this condition. Depending on the type and severity of the disease, the treatment may include:
- Medication methods;
- Surgical intervention;
- Physiotherapy;
- Antiepileptic drugs;
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet medicinal products;
- Antihypoxants;
- Nootropics and peptide drugs including Cortexin [4].
In 2013 Russian researchers conducted a nationwide screening of the cognitive and affective disorders in the process of Cortexin therapy of discirculatory encephalopathy (DEP). 50,000 patients diagnosed with DEP developed against the background of arterial hypertension and/or atherosclerosis received Cortexin in the dosage of 10 mg/daily for 10 days.
The results of the study showed some good after-effects:
- First of all there was a regression of focal neurological symptoms,
- Secondly, the patients showed an improvement of cognitive functions in neuropsychological tests,
- Besides, the emotional state of the patients was normalized,
- And there was a decrease in the level of depression. [18]
We would like to stress that encephalopathy is a serious neurological condition. But if the symptoms are detected early, there are better chances of recovery. And Cortexin is one aspect of the complex treatment of this disease.
Please note that Cortexin shall be used only according to the prescription by the attending physician. Always follow the dosage recommendations indicated in the instructions to achieve the desired effect and to minimize the possibility of adverse reactions.
HOW TO USE CORTEXIN CORRECTLY?
Cortexin goes in packs containing 10 vials containing powder for solution. There are two forms of release:
- Vials containing 5 mg of the active substance which are mainly used for children.
- Vials with 10 mg of the active substance – for adults.
CORTEXIN DOSAGE RECOMMENDATIONS
The producer recommends the following dosages:
- Adults – 10 mg once a day for 10 days. The course can be repeated after 3-6 months.
- Adults in the acute and early recovery periods of stroke – 10 mg twice a day (in the morning and in the afternoon) for 10 days. The course is repeated after 10 days.
- Children whose weight is less than 20 kg – 0.5 mg/kg once a day for 10 days. The course can be repeated after 3-6 months.
- Children whose weight is more than 20 kg – 10 mg once a day for 10 days. The course can be repeated after 3-6 months.
Cortexin shall only be used in accordance to its indications (neurological conditions) as prescribed by your doctor. Always follow the dosages indicated in the instructions to benefit from the treatment and minimize the possibility of adverse reactions.
HOW TO PREPARE CORTEXIN SOLUTION?
The route of administration of the drug is intramuscular (IM). Follow these steps ⬇️
- To make the solution use water for injections, 0.5% procaine (novocaine) solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
- With a sterile syringe, draw up 1-2 ml of liquid. *By injecting the mixture diluted with local anesthetic, the injection will be less painful. But in this case the risk of developing undesired allergic reactions is higher.
- Remove the foil from the Cortexin bottle and insert the needle through the stopper. It is recommended to lower it to the middle of the bottle and lean against the wall to reduce foaming.
- Then slowly push the plunger until the contents of the syringe are inside.
- Without removing the needle, shake the bottle with the mixture until all the powder is dissolved.
- Pull the plunger towards you until the contents of the vial are inside the syringe.
It is recommended to prepare the solution right before an injection.
The solution shall not be mixed with other medicines. Otherwise the active ingredient may lose its therapeutic properties or cause adverse reactions.
HOW TO INJECT CORTEXIN?
All manipulations are carried out in sterile gloves.
First, you need to choose the site where the injection will be made. It can be:
- Hip,
- Deltoid,
- Femoral, front thigh.
It is preferable to choose the gluteal region. The buttock is mentally divided into four squares. The injection is placed in the upper outer square. It is better to alternate the injection sites. For example if yesterday you made an injection in the right buttock, today – do it in the left one.
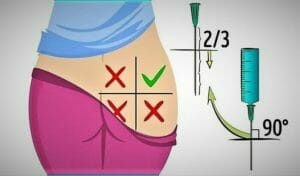
- Before injection, treat the selected site with a cotton swab dipped in medical alcohol. Wipe in a circular motion from the center to periphery.
- Before starting the procedure, tap the syringe slightly, lifting it up the needle. Then slightly press the plunger until all the air is out of the syringe.
- Stretch the skin at the site of the intended injection with your hand. Take the syringe in another hand, lift it up a little and sharply insert the needle at 2/3 of its length. During the injection, insert the needle perpendicular to the surface of the body.
- The injection shall be quick, because if you insert the needle slowly, it will be more painful.
- Then press down on the plunger to slowly get the medicine into the muscle. The optimal injection rate is 1 ml in 10 seconds.
- After that, quickly remove the needle and put the cap on it. Only in this form can the syringe be disposed.
- It is recommended to massage the injection site so that the drug is better absorbed into the tissue. Re-treat the area into which the injection was made with a cotton swab dipped in an alcohol solution. This is done in order to prevent infection.
The medicine is best taken before lunch, like any nootropic drugs.
FAQs ABOUT CORTEXIN
HOW SOON WILL I FEEL THE EFFECTS OF CORTEXIN?
Cortexin begins to take effect only a few days after the start of use. So do not stop the treatment if you do not see a quick result.
The maximum treatment effect of Cortexin usually develops by the end of the course. Cortexin is known for the long retention of the treatment effect and its potentiation in repeated courses.
WHAT ARE CORTEXIN SIDE EFFECTS?
Cortexin is a medicinal product, which means that it, like many other drugs, has certain side effects. It should be noted that the incidence of side effects in the case of Cortexin is usually low.
With strict adherence to medical prescriptions (dosage, frequency of intake, etc.), undesirable reactions are not likely. [11]
CAN I BE ALLERGIC TO CORTEXIN?
To reduce the possibility of developing allergic reactions, during the manufacture of Cortexin chemical, thermal and vacuum treatment of the original substrate occurs.
However, Cortexin is still a drug of animal origin. This means that there is still a risk of developing allergic reactions. The degree of their severity can be different: from a minor rash and mild stool disorder to generalized edema and anaphylactic shock.
Therefore, the use of any drugs (especially of animal or plant origin) in persons with a history of allergies shall always be carried out with the utmost caution after consulting an allergist. The patient shall pay close attention to the body sensations that may appear after the first injection.
The development of adverse reactions was not recorded when administering Cortexin to children. [9]
CAN I TAKE CORTEXIN IF I HAVE HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE?
Cortexin is used in the treatment of cerebral circulation disorders, asthenic conditions, and alcohol intoxication. These pathologies are often accompanied by hypertension in patients. Nevertheless cases of undesirable effects of the drug in this category of patients have not been reported. However in some clinical studies, a slight hypotensive effect of Cortexin was observed. [6]
It shall be noted that at increased pressure many tissues experience hypoxia. And Cortexin is known to increase resistance to hypoxia.
CAN I TAKE CORTEXIN WITH ALCOHOL?
Cortexin is widely used to treat post-withdrawal disorders such as severe hangover, chronic alcohol intoxication, and alcoholic encephalopathy. Also, with the simultaneous use of alcohol and Cortexin, the damaging effect on the brain decreases. And, in general, the toxic effect of alcohol is known to be lower.
Thus, Cortexin can reduce the damaging effect of alcohol on the brain, both with their simultaneous use and with the use of the drug after some time. However, the purposeful simultaneous use of Cortexin and alcohol is undesirable, since this combination reduces the therapeutic effect of the drug.
CORTEXIN DRUG INTERACTIONS
Speaking of any medicine, the question arises of how it will interact with other drugs. It depends on whether it is possible to use the drug as part of complex therapy and whether it can be used to treat a person with several different diseases.
Cortexin is a nootropic used to treat lesions of the nervous system. The list of indications for use is very diverse and includes a wide variety of diseases. Usually, they require complex therapy. [13]
These are the drugs that Cortexin is most often stacked with [16]:
Combinations of these drugs are commonly used to treat neurological conditions. Let us take a closer look at the interaction of Cortexin with each of these drugs.
CORTEXIN AND MEXIDOL

Both drugs are produced in Russia and showed efficiency in the treatment of diseases associated with damage to nerve structures: cognitive disorders, encephalopathy, cerebral circulation disorders (heart attack, ischemia), etc.
Both Cortexin and Mexidol have a proven positive effect in the treatment of alcohol intoxication, relief of withdrawal symptoms, and post-withdrawal states. [3] [15]
The area of application of Cortexin is shifted towards purely neurological diseases, while Mexidol – towards the consequences of damage to body tissues of various nature. The combined use of the two drugs increases the overall positive effect. [13]
CORTEXIN AND CEREBROLYSIN
Both drugs have a similar composition – they are polypeptides of the cerebral cortex of animals. However, there is a difference: Cortexin has a significantly larger amount of peptide fractions (90%) and fewer amino acids (10%). [17] While the former is produced from pig brains only, the latter is extracted mostly from young horned cattle cerebral cortex by acetic acid extraction.
Both drugs are successfully used in the treatment of neurological diseases. Their use in the recovery period after a damaging effect on the brain accelerates the recovery processes and promotes rapid rehabilitation. But according to the Cortexin manufacturer, it is preferred for depressive disorders, increased excitability, and fatigue while Cerebrolysin is best for the treatment of dementia of various etiologies. [16]
No adverse reactions were found when using Cortexin, except for rare cases of allergy. It should be noted that the list of side reactions of Cerebrolysin is more extensive (official instruction).
CAN I STACK CORTEXIN AND CEREBROLYSIN?
Experts do not consider it rational to combine these drugs, but quite often recommend using them in succession or alternating courses.
There is a post in the CosmicNootropic blog containing a video interview with a medical professional talking about the differences between Cortexin and Cerebrolysin. The video is translated into English.
CAN I STACK CORTEXIN AND CERAXON?
Ceraxon is also a nootropic. However, its mechanism of action is completely different.
Ceraxon is a precursor substance for fats, from which cell membranes, including nerve membranes, are built. Due to this property, the use of this drug reduces the damaging effects on nerve cells and helps to accelerate their recovery.
With the simultaneous use of Cortexin and Ceraxon, the overall positive effect is enhanced. [12]
CAN I STACK CORTEXIN AND PANTOGAM?
Pantogam is a medicine that contains hopantenic acid. This acid is a nootropic with a mild stimulating effect, which is manifested by the acceleration of the processes occurring in the brain.
This ensures the normalization of the brain processes and contributes to the rapid restoration of nerve structures when they are damaged.
According to information from the manufacturer, with the simultaneous administration of Cortexin and Pantogam, the therapeutic effect will be more pronounced. [16]
CAN I STACK CORTEXIN AND CAVINTON?
Cavinton is a nootropic as well. And it has several indications for use.
Firstly, this drug improves blood supply to the brain by reducing blood viscosity and accelerating the process of oxygen transfer to the nerve cells. Secondly, Cavinton reduces the damaging action of excitatory amino acids on nerve cells, providing a neuroprotective effect.
According to the producer, the simultaneous administration of Cortexin and Cavinton will have a more pronounced positive effect than their separate use. [16]
INFORMATION ABOUT CORTEXIN PRODUCER – GEROPHARM
Cortexin is manufactured by GeroPharm. It is a large Russian pharmaceutical organization that has existed since 2001.
GeroPharm works in different directions, implementing projects under the programs of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation. The company has representative offices in several countries and across Russia.

The company product portfolio includes:
- Neurology (Cortexin, Recognan, Levetinol, Memantinol).
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (Pineamin, Epifamin).
- Ophthalmology (Retinalamin).
- Endocrinology (Rinsulin).
Besides it is worth noting that it was GeroPharm that launched the only full-cycle industrial production of synthetic insulin in Russia.
GeroPharm is one of the largest investors in the field of technological innovation and R&D. The company has repeatedly become a laureate and prize-winner of various awards, contests, and ratings:
- Prize in the field of import substitution “Priority” (2015),
- Competition “Leader of the Russian business” (2016),
- Competition “Development Award” (2016),
- Gazelle business (2016, 2017),
- Enterprise of the Year (2016, 2017),
- EY Entrepreneur of the Year (2017),
- RBC award (2017).
ANECDOTAL CORTEXIN REVIEWS
There are many discussions on the effectiveness of Cortexin in comparison to other nootropics like Cerebrolysin. Opinions differ but it can be said that there are positive reviews on both. Since this article is devoted to Cortexin we would like to focus on its reviews.
For example, there is a positive Cortexin experience on Reddit in regards to cognitive improvement. Besides Cortexin is known to help recover from drugs and other additions. Many nootropic enthusiasts use it for these purposes in combination with other medications. Doses and stack combinations are actively discussed on Reddit. There is a post about stack advice from nicotine addiction.
There are some references on the Cortexin product page at CosmicNootropic. Also according to the statistics report, Cortexin is on the list of the TOP 10 most popular nootropics in Russia.
You may get yourself familiar with Cortexin experience reviews on a Russian popular platform Otzovik.ru.
There is also a subreddit devoted to r/Cortexin peptide! Here we publish research and other relevant information about this peptide. You are welcome to join in!
The official drug sheet of Cortexin
The use of any drug shall always be medically justified. Thoughtless use of medicines can cause harm. Only a doctor has the right to prescribe medication.
Cortexin Review: Bibliography
- Tsyganov VN, Bogoslovskiĭ MM (2004). Influence of cortexin on memory and attention. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15537099/
- Skoromets AA, Dyakonov MM (2005). Cortexin. Five years of experience in Russian neurology. https://geropharm-ru.translate.goog/portfolio/nauchnyye-publikatsii?_x_tr_sl=ru&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=ru&_x_tr_pto=nui
- Alekhnovich AV, Ivanov VB et al (2005). Cortexin use in cases of acute intoxication with psychopharmacological substances. https://geropharm.ru/uploads/multimedia/parsed/pdf/ae8fbb86a1d82026adcd7a3befdec21c.pdf
- Solov’ev AG, Elistratova TV (2010). Effectiveness of cortexin in the complex treatment of patients with chronic alcohol encephalopathy and polyneuropathy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20517210/
- Stakhovskaya LV, Meshkova KS et al (2012). A multicenter, randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the safety and efficacy of Cortexin in the acute and early recovery period of hemispheric ischemic stroke. https://geropharm.ru/uploads/multimedia/parsed/pdf/4cf771e40cf71a28d1b81c94412d1c29.pdf
- Podsonnaya IV, Efremushkin GG (2016). The efficiency of cortexin in hypertensive patients exposed to radiation. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/effektivnost-korteksina-pri-lechenii-arterialnoy-gipertenzii-u-bolnyh-podvergshihsya-ioniziruyuschemu-izlucheniyu-v-anamneze
- Kholin AA, Zavadenko NN et al (2017). Peptidergic nootropic therapy in cerebral palsy associated with epilepsy. https://doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20171179137-42
- Fedin AI (2018). The efficacy of Cortexin and Memantinol (Memantine) in the treatment of cognitive impairment in patients with chronic cerebral ischemia. https://doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20181181130-36
- Zykov VP, Serebrennikova EB et al (2018). Results of a multicenter study on the efficacy of cortexin in treatment of cognitive dysfunction in children. https://doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20181183127-31
- Bogacheva TE, Kalacheva AG et al (2018). Neuroprotective and anticonvulsant effects of Cerebrolysin in the experiment. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/neyroprotektornoe-i-protivosudorozhnoe-deystvie-tserebrolizina-v-eksperimente
- Gulyaeva NV (2019). Molecular mechanisms of brain peptide-containing drugs: cortexin. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11055-019-00839-4
- Belova LA, Mashin VV et al (2019). A multicenter observation study of the efficacy of cortexin and recognan (citicoline) in the treatment of cognitive impairments in chronic cerebrovascular pathology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30874524/
- Safronova MN, Kovalenko AV, Mizurkina OA (2019). Combined neuroprotection in the treatment of post-stroke aphasia. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31464285/
- Khabirov FA, Khaibullin TI et al (2020). Comparison of the efficacy of Cellex and Cortexin in patients in the early recovery period of ischemic stroke. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33449527/
- Volchegorskii IA, Izarovskii BV et al (2021). An effect of 3-oxypyridine and succinic acid derivatives on the time of reduction of anxiety and depression symptoms in alcohol withdrawal treatment. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34693691/
- Official product web-page: https://korteksin.ru
- Gomazkov OA (2015). Cortexin: molecular mechanisms and targets of neuroprotective activity. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26356623/
- Manasyan AM et al (2014). An open clinical trial of cortexin in treatment of brain ischemia. https://www.mediasphera.ru/issues/zhurnal-nevrologii-i-psikhiatrii-im-s-s-korsakova/2014/9/downloads/ru/031997-7298201499








